Advantages and disadvantages of RJ45 integrated network transformer
Advantages and disadvantages of RJ45 integrated network transformer
Comparison of wiring and design between RJ45 with network transformer and without network transformer
The RJ45 connector is the core interface of Ethernet communication. Depending on whether the network transformer (Magnetics) is integrated, its design can be divided into two types: **integrated (with network transformer) and discrete (without network transformer)**. The two solutions differ significantly in circuit design, wiring complexity, cost, and performance. The following details its advantages and disadvantages from the perspective of wiring and design.
────────────────────────────────────────────────
1. Integrated RJ45 (with network transformer)
1. Advantages
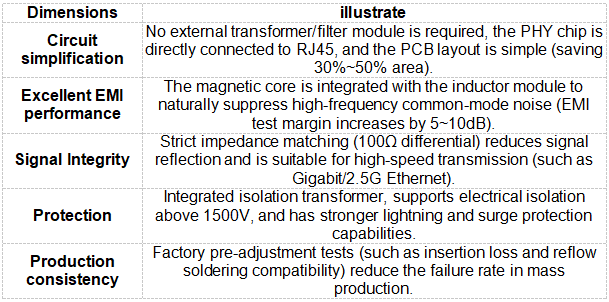
2. Disadvantages
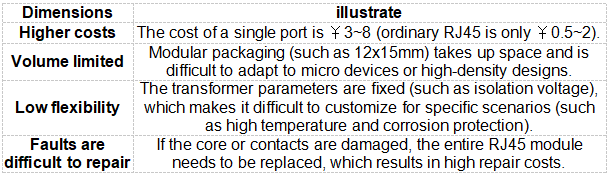
Typical applications: industrial control equipment (such as PLC), Gigabit switches, industrial-grade PoE power supply equipment.
────────────────────────────────────────────────
2. Discrete RJ45 (without network transformer)
1. Advantages
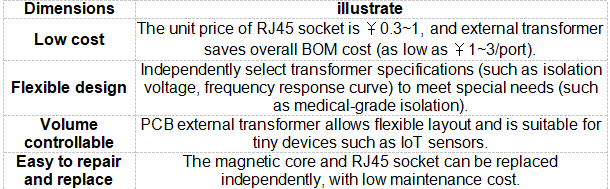
2. Disadvantages
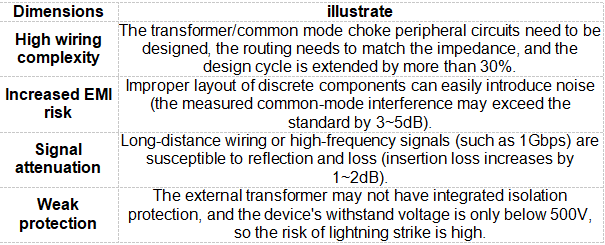
Typical applications: consumer routers, home security equipment, low-speed (10/100Mbps) industrial control terminals.
────────────────────────────────────────────────
3. Comparison between wiring and design
1. Circuit design complexity
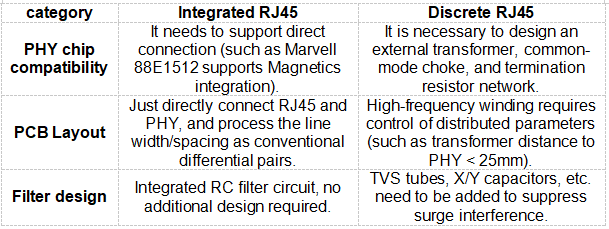
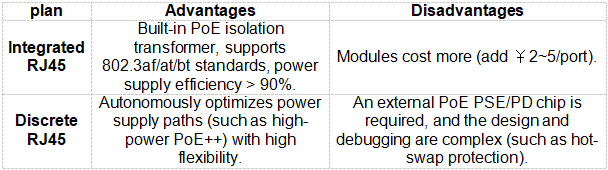
2. PoE power adapter
3. High frequency performance (taking 1Gbps as an example)

────────────────────────────────────────────────
IV. Application scenario recommendations
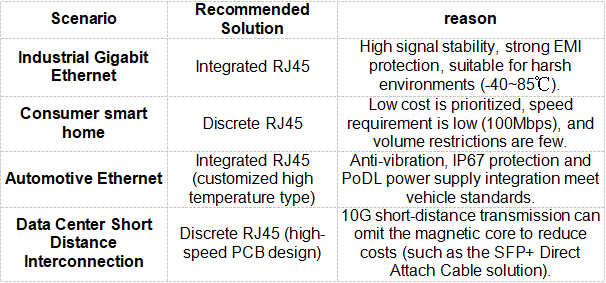
────────────────────────────────────────────────
V. Conclusion
The advantages of integrated RJ45 (with network transformer) are simplified design and improved reliability, but the cost and volume are relatively high; discrete RJ45 (without network transformer) has advantages in cost control and flexibility, but requires more design resources.
Core decision factors
- Cost priority: Discrete type is preferred for mass production, and integrated type is selected for high-end scenarios.
- Speed and distance: For Gigabit/long distance, integrated type must be selected; for 100M/short distance, discrete type can be considered.
- Environmental requirements: Industrial-grade EMC/protection requires integrated type, while consumer electronics can choose discrete type.
Future trends: As the cost of 10G PHY decreases, integrated RJ45 is expected to replace discrete solutions in more fields, driving the Ethernet interface towards modularization and high integration.
Newsletter subscription
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated on the latest information of our company and product.
Name
|
I agree that the information that I provide will be used in accordance with the terms of Voohu International Inc. Privacy & Cookies Policy






















